Islet Transplantation in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus With Hypoglycaemic Unawareness
Case Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37707/jnds.v1i4.74Keywords:
type 1, diabetes, hypoglycaemia unawareness, islet cell transplantation, beta cellAbstract
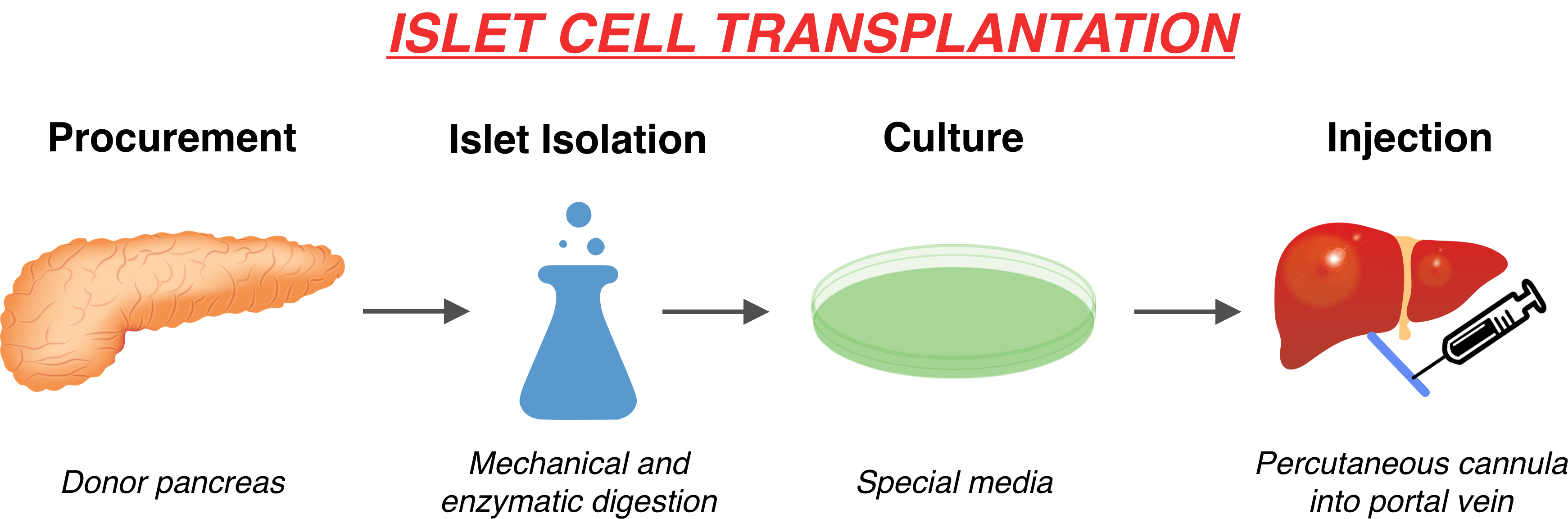
- The primary indications for ICT in T1DM are glycaemic lability and hypoglycaemia unawareness.
- ICT is an effective, minimally invasive treatment for stabilising glycaemic control, correcting hypoglycaemia unawareness and improving quality of life even when exogenous insulin-independence is not fully achieved. However, the majority of patients require two islet transplants.
- The need for lifelong immunosuppression, in combination with the limited availability of donor pancreases, currently limits the wider application of ICT, particularly in the treatment of children newly diagnosed with T1DM.
- New technologies, including macro- and micro-encapsulation, xenotransplantation and stem cell-derived b cells offer hope for the future of b cell replacement. Yet, until then, a continued focus on optimising donor pancreases, improving the islet isolation procedure, use of novel immunosuppression, and understanding the mechanisms behind graft loss is required.
Published
2020-06-30
Issue
Section
Case Studies
License
Authors will retain copyright alongside scholarly usage rights and JNDS will be granted publishing and distribution rights.